Tabulation of raw data and graphical representation
统计信息:具有特定目的的数据收集过程并回答问题称为统计。
或者
The process of drawing facts from numerical data. It includes the collection of the data, presentation of the data and Interpretation of the data.
观察:数字图的形式的信息称为观察。
Statistical Data and Collection: The facts collected for the purpose of investigation is called statistical data.
There are two types of data:
(i) Primary data
(ii) Secondary data.
Primary data: The data-collected by the investigator for the first time for his own use.
次要数据:除研究者以外的次级源收集的数据,例如
原始数据:从原始源获得但未正确安排的数据称为“原始数据”。
Array: Raw data does not provide any useful information but it creates confusion. The data in the above form is called 'ungrouped data'. An 'array' is an· arrangement of raw numerical data in he ascending or descending order of magnitude.
分组数据:可以在组或类别中系统地放置数据。
一些事实
变量:从观察到观察的数量称为变体。
范围:最大观测和最小观测之间的差异称为范围。
Class-interval: Datas are divided in groups, each group is called an interval or class i.e., the upper limit and lower limit of a class constitutes a class-interval. It is also called as class-size.
类限制:每个类互助都有两个限制。间隔的最小观察称为下限,间隔的最大观察称为上限。
Class-size: The difference between the upper and lower limits of interval is called class-size or the difference between two successive class-marks is called class-size.
Class-mark: The mid-value of the class is called its class-mark.

频率:计数标记的计数或特定类中的观测值称为其频率。
类频率:类的相应 - 频率称为其类频率。
频率分布表:在许多类中分布频率的表格称为频率分布。
Cumulative frequency: The cumulative frequency of a class is the sum of all frequencies prior to that class.
独家方法:在此方法中,每个类的上限是下一类的下限。
Inclusive method: In this method, the upper limit of none of the classes is the lower limit of the next class.
例如:此方法中的类将为:0-4、5-9、10-14、15-19、20-24、25-29。
Presentation of Data: to convert a -aw or an ungrouped data into grouped data.
Step 1. Determination of the range.
Step 2. Fixation of Class-interval: There is not hard and fast rule of
determining the number of classes. It is advisable to have total number or classes between 5 and 15.
Step 3. Fixation of Class-size:
Divide the range by the desired number of classes to determine the approximate size of the class interval.
步骤4.查找类限制。课程不应重叠。两类之间不应存在差距。
Classes should be of uniform (or same) size.
开放式班级,例如少于5或超过10的班级等不应使用。
We take each observation from the data one at a time and place a tally mark 'l' opposite the class to which the item belongs by cuting the numbers from the data.
特定类中的计数标记的计数告诉该类的频率。所有频率的总和应等于观测值的总数。
图表表示:
Column Graph: In both the bar graph and column graph, the bars or columns are equally wide.
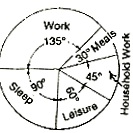
馅饼图是通过绘制半径划分为扇区的圆。
The central angle of a sector will be proportional to the time for the corresponding item.
无需输入每个角度的测量。
Histograms: Histograms is a graphical representation of the frequency distribution of a continuous variable. In the construction of histograms, class-intervals of continuous data are taken on X-axis and then rectangle of appropriate height such that area of the histogram is equal to the frequency of that class interval are erected over them.
\ Height of rectangle
类间隔的类频率/宽度
如果所有类区间的宽度是山姆e then the height of the rectangles can be taken in proportion to the frequency.
“整个频率分布直方图的总面积等于HE频率分布中的项目总数。
频率多边形:通过连接直方图中矩形的相应顶部的中点获得频率多边形。终点在两端都扩展到连接X轴。X轴和曲线的两个极端之间的图形面积等于数据的总频率。在频率中,x-corm对应于多边形中最高点的值将等于模式。
Note: To complete the polygon, the mid-point at each end is joined to the mid-point of the immediately lower or higher imagined class interval as the case may be at zero frequency. Note that this ensures that the total area of a frequency polygon is the same as that of the corresponding histogram.
累积频率曲线或OGIVE:就像频率多边形的直方图是频率分布的图,累积频率曲线或OGIVE是累积频率分布的图。
小于Ogive:在分组的频率分布的情况下,累积频率曲线是通过该点绘制的自由手平滑曲线,该曲线具有类相关的上限为脓肿及其相应的累积频率作为坐标。
不仅仅是Ogive:它是一条通过横坐标及其相应的累积频率作为坐标的较低点的自由手平滑曲线。
速度时间图:当速度保持恒定时(无加速度)。
When velocity changes in a non uniform way (non-uniform acceleration).
In a velocity-time graph, the area enclosed by the velocity-time curve and the time axis gives the distance travelled by the body.
Velocity-time graph when velocity changes at a uniform acceleration: A straight line sloping upwards shows uniform acceleration, whereas a straight line sloping downwards indicates uniform retardation.
当加速度non-unifo速度-时间图rm: Here also the distance travelled is given by the area between the velocity-time graph and the time axis.
Distance/Displacement-time graph: The slope of a distance-time graph indicates velocity. The velocity of the body is non-uniform, then the graph between distance and time is a curved line called a parabola as shown in the figure.
TEMPERATURE SCALES
华氏度量表:在其上,下固定点为32°,上固定点为212°,因此在两个固定温度之间存在212-32 = 180相等的分裂。
Celsius scale: On it, the lower fixed point is taken as 0° and the upper fixed point is taken as 100°, so that there are 100 - 0 = 100 equal divisions between two fixed temperatures.
在比较这两个量表时,我们发现
0°C = 32°F
100°C = 212°F
Relationship between Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales of Temperatures.
从华氏度到摄氏量表C = 0.556×(F -32)
从摄氏温度到
Fahrenheit scale F = 1.8 C + 32
其中f =温度。在华氏度量表上c =温度。在摄氏量表上。
Live Math Experts: Help with graphical representation Assignments - Homework
Expertsmind.comoffers help with graphical representation assignment and homework in mathematics subject. Experts mind's数学experts are highly qualified and experienced and they can solve your complex graphical representation math problems within quick time. We offer email based assignment help -homework help service in all math topics including graphical representation .
数学在线辅导:图形表示
我们在Expertsmind.comarrange instant online tutoring session in graphical representation math topic. We provide latest technology based whiteboard where you can take session just like live classrooms.数学ExpertsMind.com的专家在图形表示数学主题中提出了明确的概念和理论,并为您提供了解决复杂图形表示问题的棘手方法。